Title
Induction of Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage, Hematological and Histopathological Effects of Silica Nanoparticles and Ethanol Solvent in Swiss Albino Mice
Authors
Sangeetha A.,a,b Samyuktha L.,a,b Atya K.,a,c Neha H.,d Rakesh K.S.,e Shantveer G.U.f and Kaiser J.*a
aCentre for Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Advanced Studies (JNIAS), Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
bDepartment of Biotechnology, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur (JNTUA), Anantapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India.
cEnvironmental Genomics Division, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research- National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (CSIR-NEERI), Nagpur, Maharashtra, India.
dCentre for Nanomaterials, International Advanced Research Centre for Powder metallurgy and New materials (ARCI), Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
eSaveetha Institute of Medical And Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Chennai-600077, Tamilnadu, India.
fDepartment of Pathology, Nizam’s Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS), Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
*Corresponding author E-mail address: kaiserjamilgene@gmail.com (Kaiser Jamil)
Article History
Publication details: Received: 14th August 2020; Revised: 05th September 2020; Accepted: 07th September 2020; Published: 12th September 2020
Cite this article
Sangeetha A.; Samyuktha L.; Atya K.; Neha H.; Rakesh K.S.; Shantveer G.U.; Kaiser J. Induction of Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage, Hematological and Histopathological Effects of Silica Nanoparticles and Ethanol Solvent in Swiss Albino Mice. Nano Prog., 2020, 2(4), 32-39.
Abstract
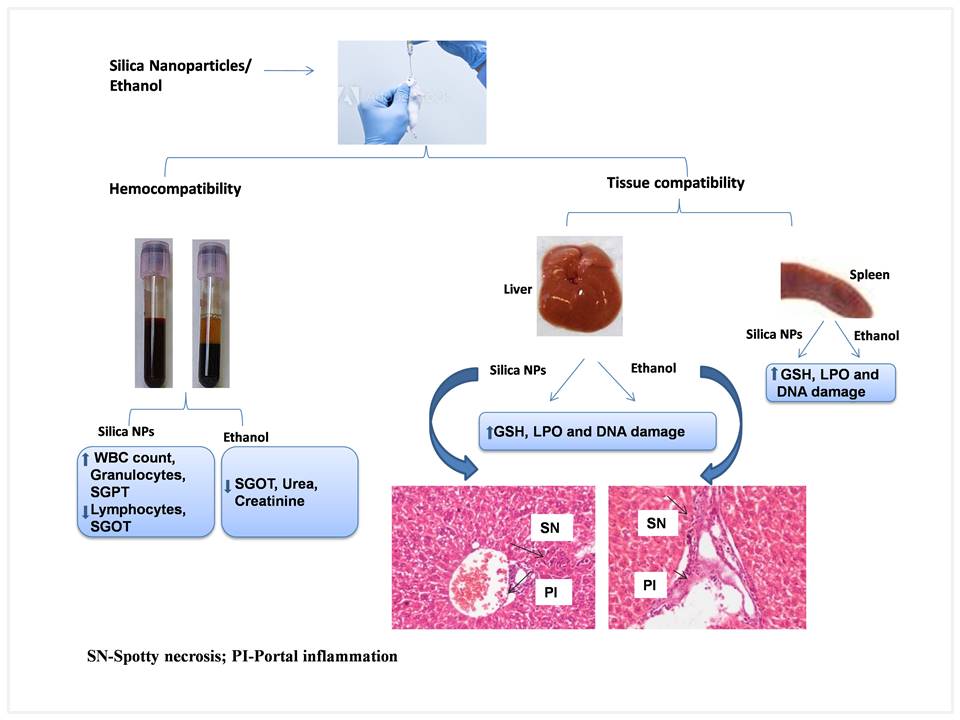
Silica nanoparticles (Silica NPs) are one of the promising candidates for biomedical applications and necessitate a systematic understanding of the NPs’ interaction with the biological machinery. In the present study, we have investigated the in vivo effects of Silica NPs and Ethanol solvent administered as acute doses to mice by oral route and assessing the haematological and serum biochemical parameters, oxidative stress, genotoxicity, and histopathological alterations. Silica NPs’ treatment was found to induce a significant (p<0.05) increase in white blood cell and granulocyte count, SGPT levels, and decrease in lymphocyte count and SGOT levels, whereas the Ethanol treatment was shown to decrease the levels of SGOT, urea, and creatinine. Remarkable change (p<0.05) in GSH and LPO levels in the liver and spleen suggest the potential of Silica NPs and Ethanol in inducing oxidative stress. Further, significant DNA damage marked from the increased comet parameters and micronuclei formation in the liver, spleen, and kidney of mice treated with Silica NPs and Ethanol indicates the genotoxic potential of these materials. Histopathological examination in mice treated with Silica NPs and Ethanol indicated (i) spotty necrosis and portal inflammation in the liver, (ii) mild red pulp congestion in the spleen, and (iii) moderate vascular congestion in the lung (Ethanol). Results obtained in the present study enlightened the need to optimize Ethanol content to minimize the toxic effects of Silica NPs. Such visions are considered to be vital for the development of performance Silica NPs for outstanding biomedical utilities.
Keywords
Silica nanoparticles; Hemocompatibility; Oxidative stress; Genotoxicity; Histopathology; Oral toxicity