Title
Cost-Effective Alumina-Polymer Nanocomposite: An Excellent Candidate for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Environmental Samples
Authors
C. M. Babu,a R. Balasubramanian,b R. Vinodh,a P. Thirukumaran,b A. Shakila Parveen,b A. Selvamani,c B. Sundaravel,d and V. Ramkumar*c
aDepartment of Chemical Engineering, Hanseo University, South Korea.
bDepartment of Chemistry, Anna University, Chennai - 600025, India.
cDepartment of Polymer Science and Technology, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) - Central Leather Research Institute (CLRI), Adyar, Chennai, 600020, Tamil Nadu, India.
dDepartment of Chemistry, Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education, Krishnan Kovil, 626126, Tamil Nadu, India.
*Corresponding Author Email Address : srirams27@gmail.com (V. RAMKUMAR)
Article History
Published details: Received: 6th February 2019, Revised: 11th February 2019, Accepted: 11th February 2019, Published: 18th February 2019
Cite this article
Babu C. M.; Balasubramanian R.; Vinodh R.; Thirukumaran P.; Shakila Parveen A.; Selvamani A.; Sundaravel B.; Ramkumar V. Cost-Effective Alumina-Polymer Nanocomposite: An Excellent Candidate for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Environmental Samples. Nano Prog., 2019, 1(1), 1-9.
Abstract
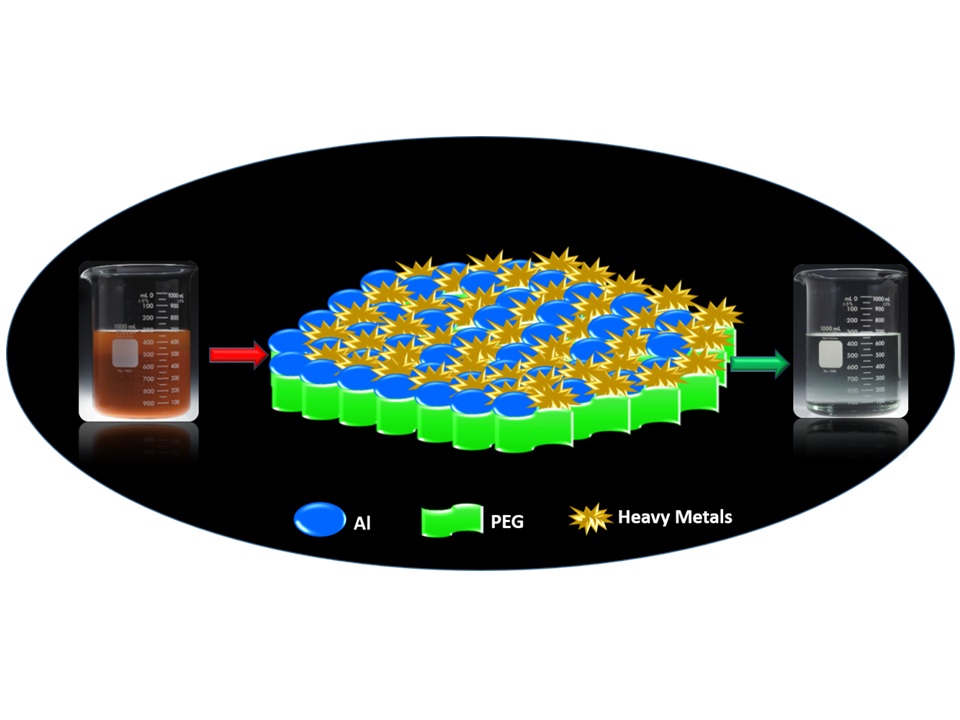
An efficient solid phase extraction method has been demonstrated for the removal and preconcentration determination of Cu (II), Co (II), Mn (II) and Cd (II) by using a new adsorbent material, alumina modified polyethylene glycol (PEG) nanocomposite (PEG-Al2O3). Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) was used to determine the concentration of metal ions adsorbed by PEG-Al2O3. Physically adsorbed metal ions from PEG-Al2O3 were eluted by using hydrochloric acid and the resultant solution was tested by FAAS. Various adsorption conditions such as effect of pH, amount of adsorbent, preconcentration time, elution time, volume of aqueous phase, and concentration of metal ion were optimized. High metal up-take was found providing this order: Cu (II) > Co (II) > Mn (II) > Cd (II) due to the strong contribution of surface loaded polyethylene glycol. Metal ions, (Cu (II), Co (II), Cd (II) and Cd (II)) containing four real samples (sea water, river water, tap water and grape juice) were studied. To our delight, the prepared PEG-Al2O3 nanocomposite was worked well towards the removal of metal ions with an excellent recovery percentage of 98-100%.
Keywords
Alumina; Polyethylene glycol; Nanocomposite; Heavy metals; Preconcentration; Real sample analysis